Solutions are formed when a solute is dissolved in a solvent.
Forming solutions
In order for a solution to form, the solute intermolecular forces must be broken as well as the solvent intermolecular forces. Then the solute and solvent form new intermolecular forces with each other. If the energy required to break the intermolecular forces is much greater than the energy released when the new forces are formed, the solution will not form.
Factors affecting solubility
For gases, as the pressure of the gas above the solution increases, the solubility of the gas increases. For gases, as the temperature of the solution increases, the solubility of the gas decreases. For most solids, as temperature increases, the solubility increases.
Concentration calculations
There are many ways to express concentration (which is the ratio of solute to solvent or solution).
% by mass: 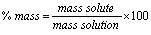
The mass units must match!
% by volume: 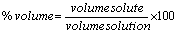
The volume units must match!
% mass/volume: 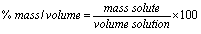
The volume unit is mL
Molarity (M): 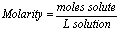
Molality (m): 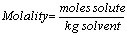
A sample becomes diluted (less concentrated) when more solvent is added. The dilution equation is
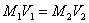 M1 = original molarity V1 = original volume M2 = new molarity V2 = new volume. Volume units must match!
M1 = original molarity V1 = original volume M2 = new molarity V2 = new volume. Volume units must match!
Colligative properties
A colligative property is a property that depends on the number of solute particles in the sample. The vapor pressure of a solution is lower than the pure solvent because the number of solvent particles on the top layer that can evaporate is lower. Because the vapor pressure is lower, the boiling point of a solution is always the higher than the pure solvent and the freezing point is always lower than the pure solvent. An electrolyte solution, one in which the solute breaks apart into multiple ions which allow electricity to be conducted, has an even greater change in vapor pressure, boiling point or freezing point because there are more particles in the solution than molecules added to the solution.
Colloids
Colloids are solutions with solute particles large enough to scatter light. They exhibit the Tyndall Effect, where light is seen traveling through and spreading out as it travels through colloid.



